What are group policies?
When making security hardening, for example, in a Windows server environment, often the same hardening settings are desired to be applied to all - not just to individual or current servers.
Group policies (Group Policy Objects or commonly GPO) are a feature of Windows that is part of Windows Active Directory. With GPOs, server administrators can centrally manage and configure operating system settings, applications, and user environments in Active Directory.
They are commonly used in business environments, schools, and other organizations where there is a need to manage large quantities of computers and users.
What can be done with GPO?
With GPOs, you can, among other things:
- Defines settings such as background image, network printers, or security updates.
- Prevent or allow access to certain programs or Windows features.
- Configure security settings such as firewall and antivirus regulations.
- Manage user profiles and login scripts.
- To perform other cybersecurity hardening measures.
How to use GPOs?
Open Group Policy Management (GPM) by searching for it with the Windows button search:
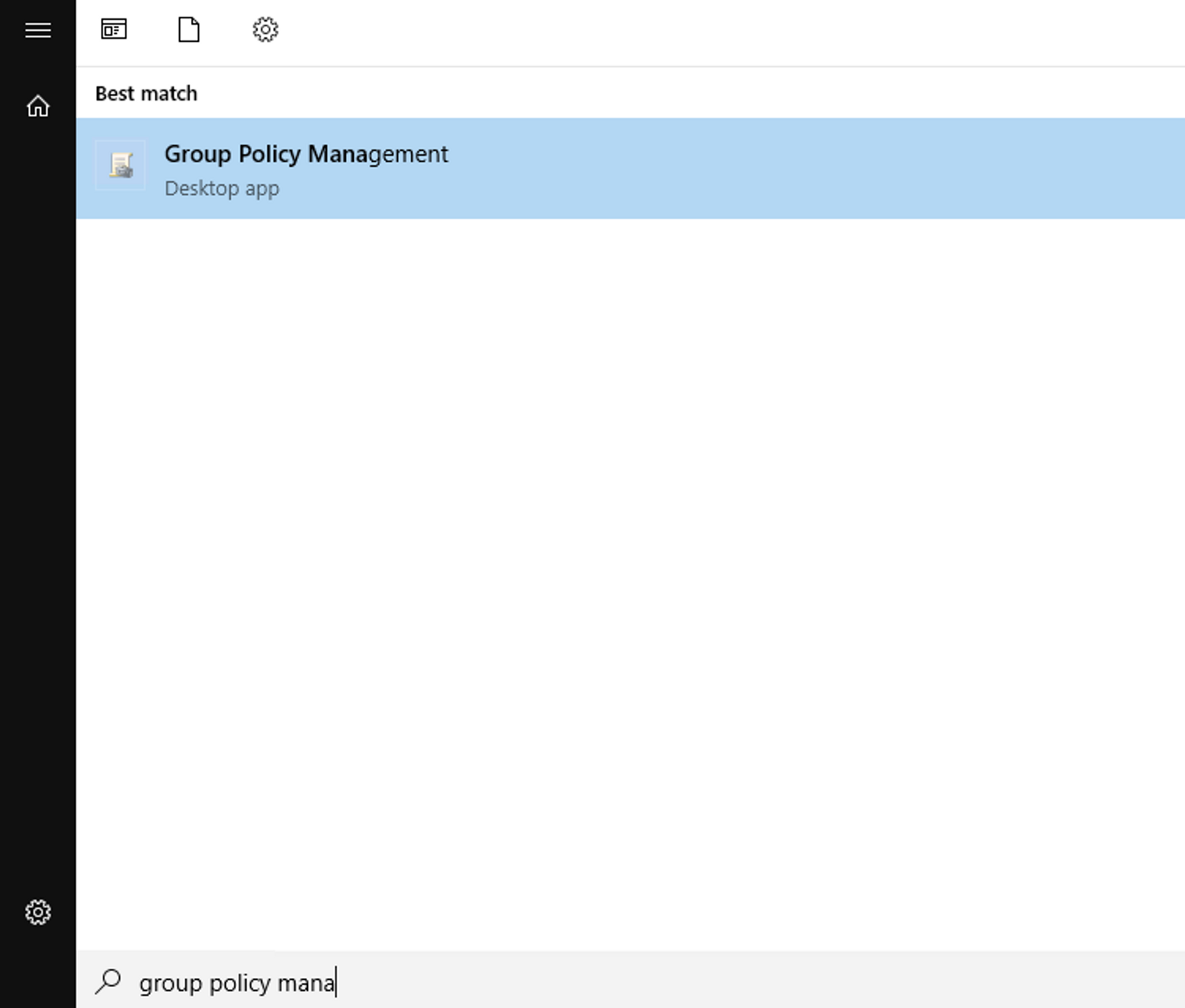
Expand the scope you want to create a GPO for. In this case, evilcorp.local.
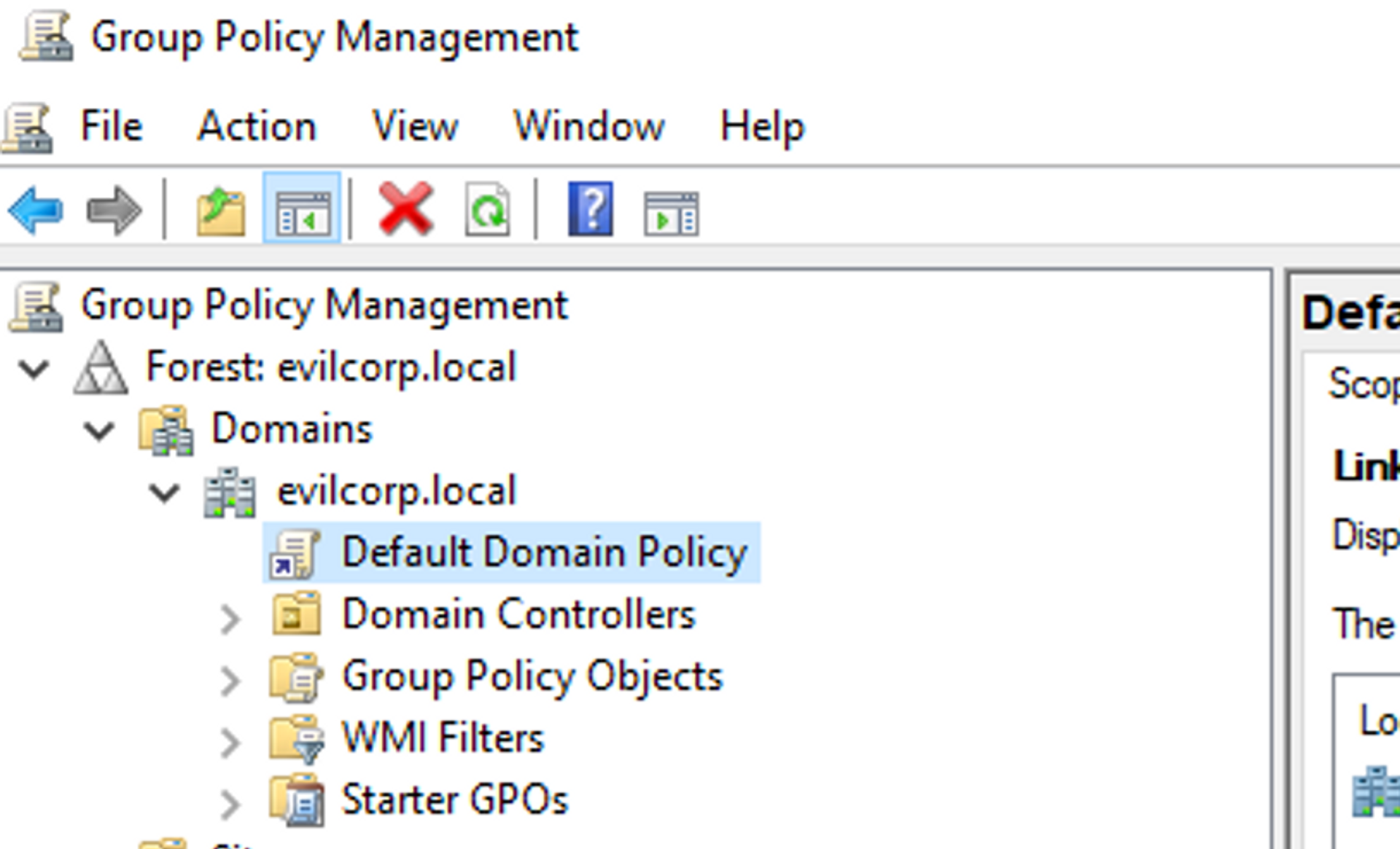
Creating a New GPO
Right-click the organizational unit (OU) you want the policy to apply to and select "Create a new GPO in this domain, and Link it here".
Modifying existing GPO
Click on GPO and select "Edit" to open the Group Policy Management Editor. From here, you can configure user and computer-specific policies. Settings are divided into two main categories: "User Settings" and "Computer Settings".
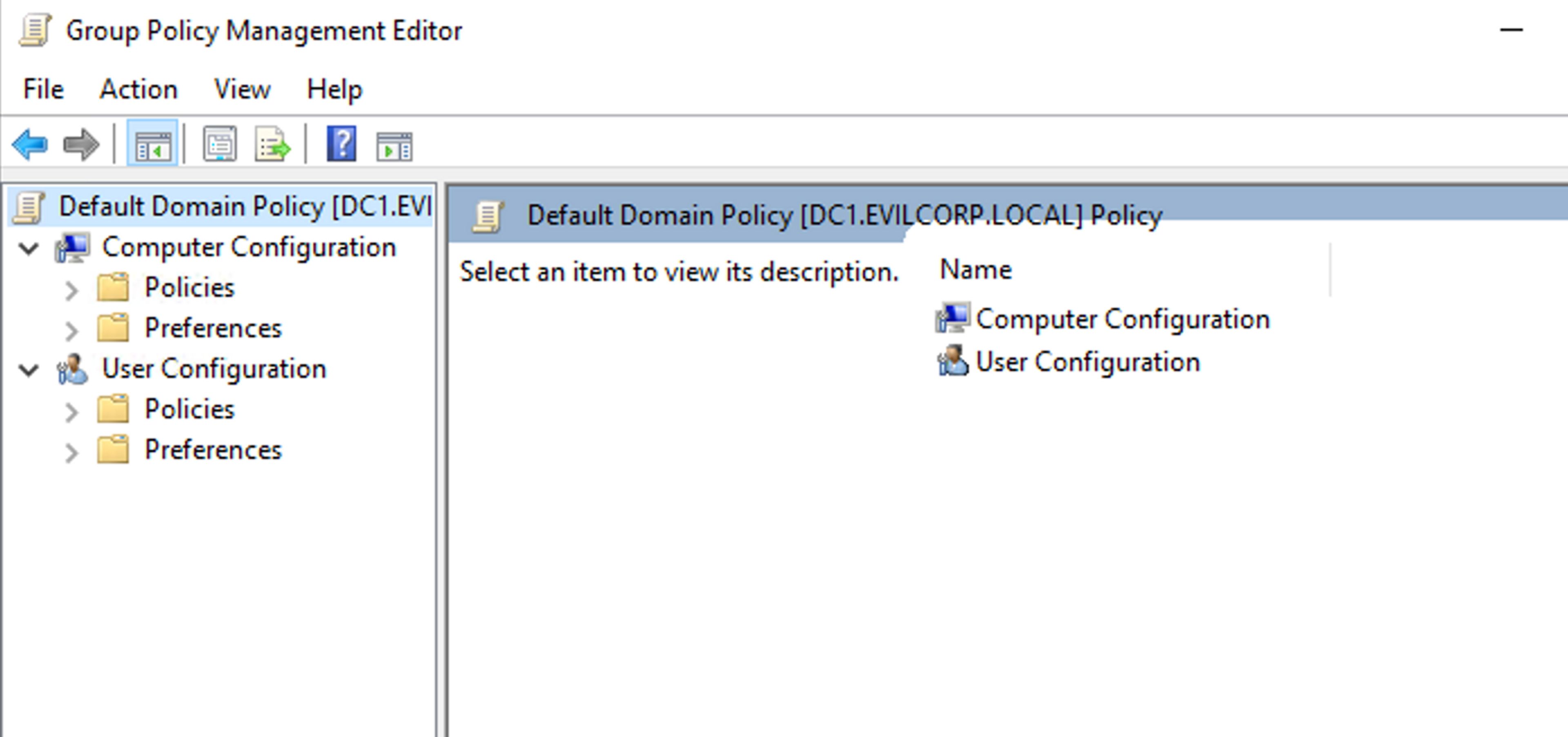
Creating a new rule
You can now edit the GPO. For example, if you want to disable the Task Manager, you can do so as follows:
- Expand the tree structure as follows: User Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Ctrl+Alt+Del Options.
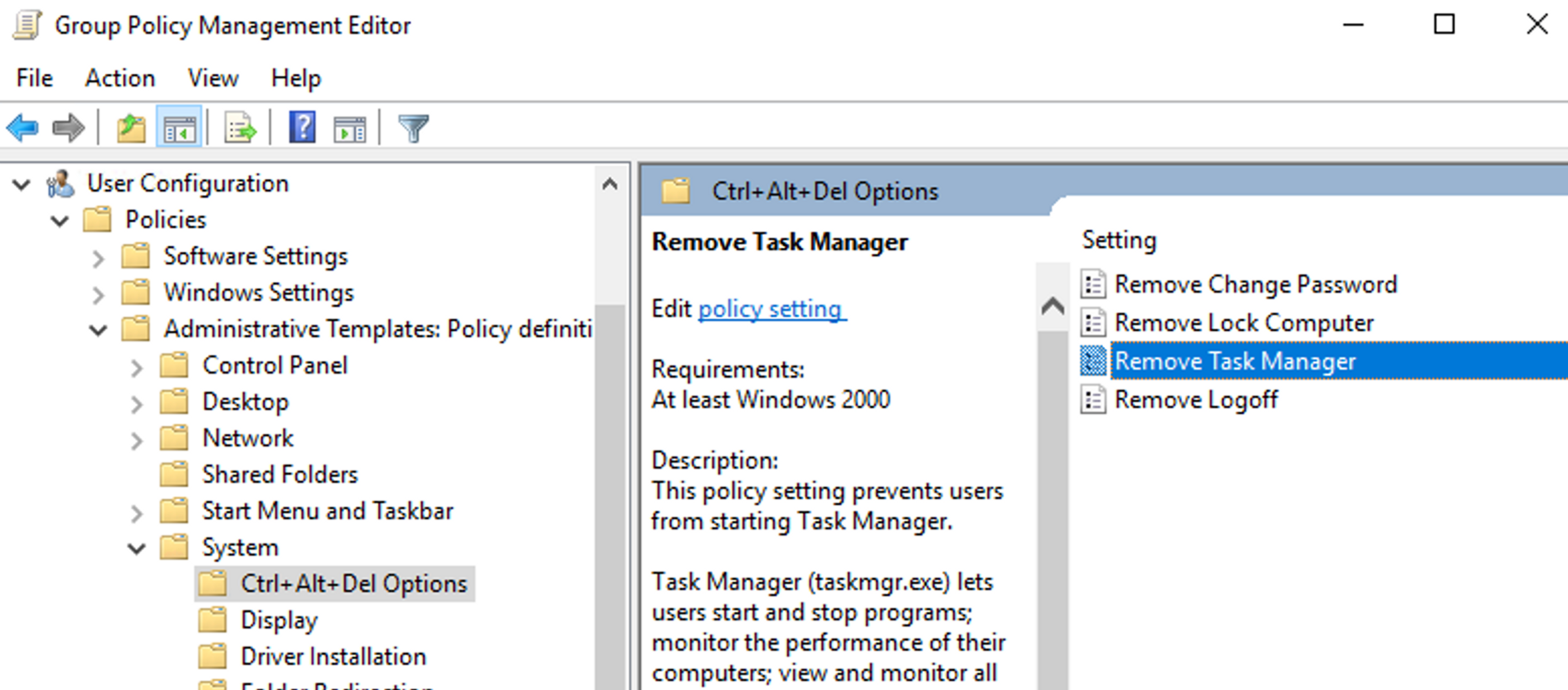
- Double click "Remove Task Manager".
- Change the value to "Enabled".
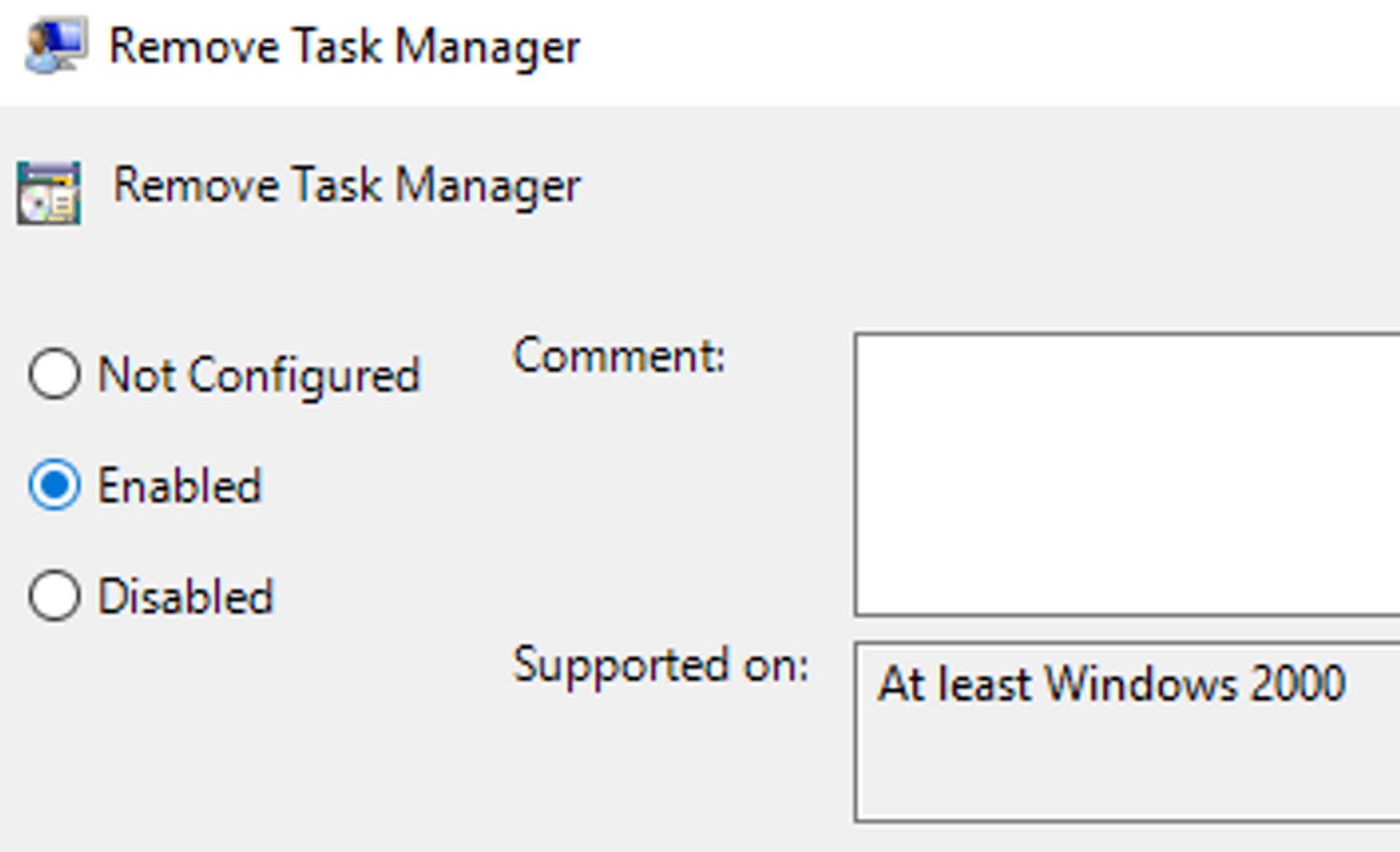
- Press "OK" in the end.
Implementation of Updated Policy
Once you have configured the desired settings, close the editor. The GPO will be automatically applied according to the schedule defined by the AD, or you can force the update by using the command "gpupdate /force" on the target machine.
Open PowerShell and run it as an administrator (right-click and "Run as administrator").
Then execute gpupdate /force
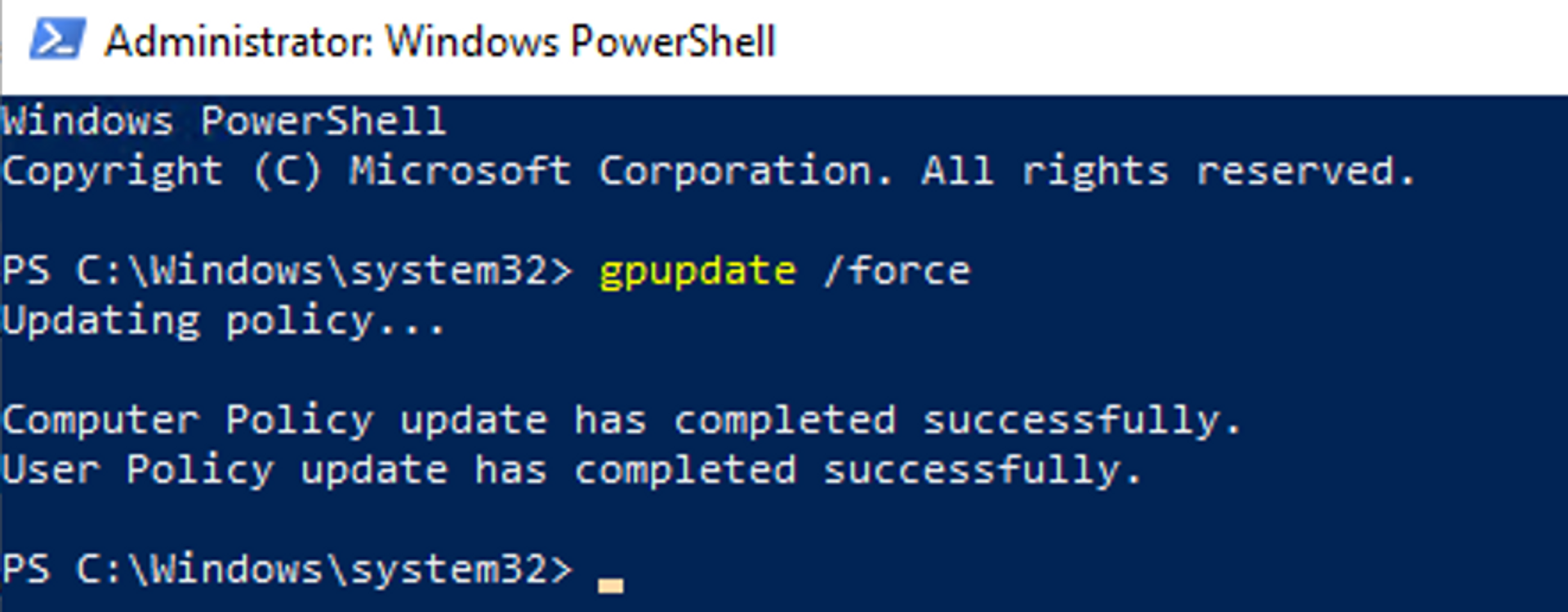
The changes should now be effective on the server on which you executed the command.
Exercise
Prevent the use of task manager as described above. Then try to open it:
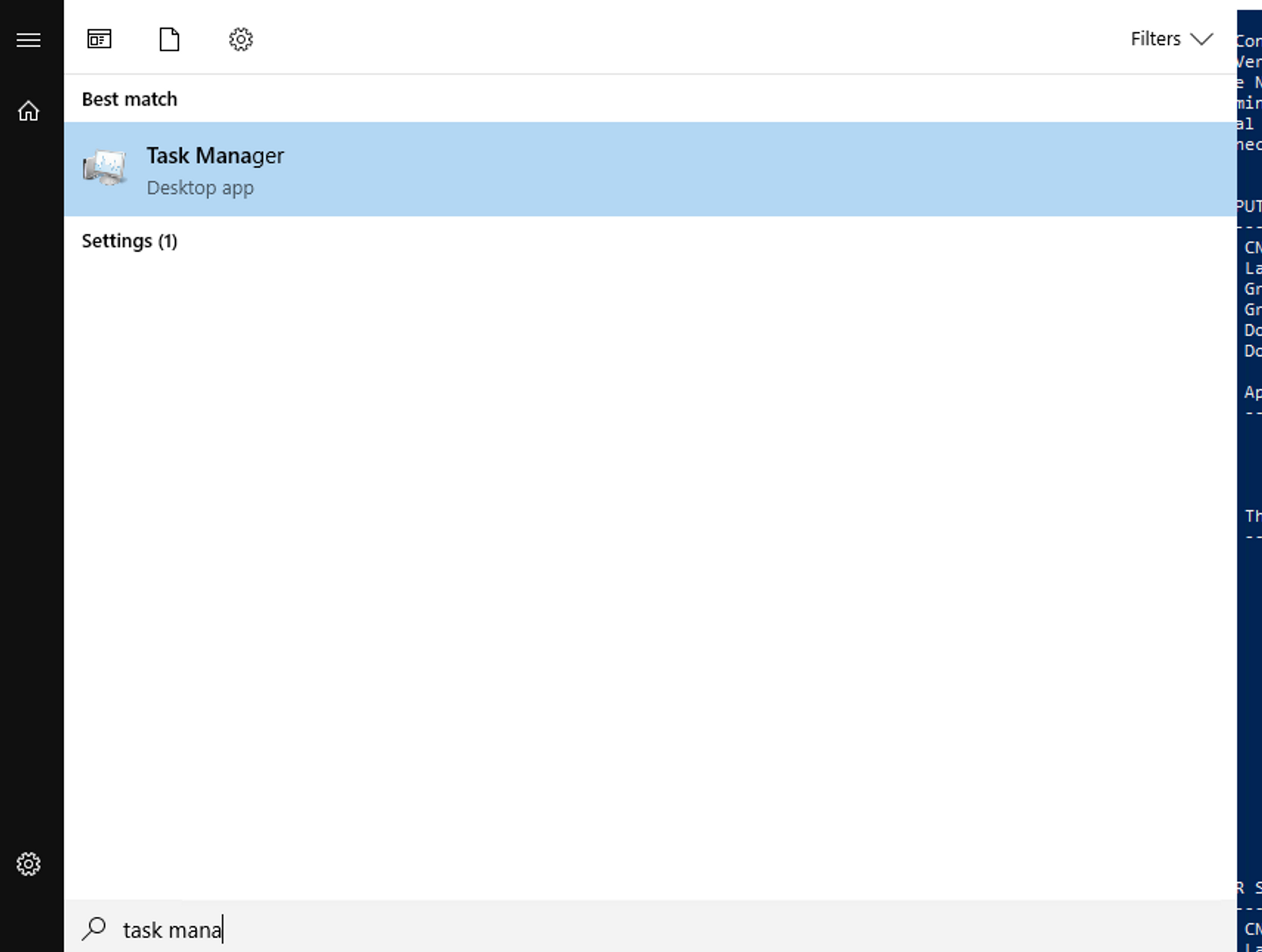
What error message are you getting?


Ready to become an ethical hacker?
Start today.
As a member of Hakatemia you get unlimited access to Hakatemia modules, exercises and tools, and you get access to the Hakatemia Discord channel where you can ask for help from both instructors and other Hakatemia members.



