What is Windows Firewall?
Windows Firewall (also known as Windows Defender Firewall in the latest versions of Windows) is a local firewall software for Windows. A local firewall means that the firewall only protects the device itself, including attacks from the same local network.
It acts as a filter for both incoming (ingress) and outgoing (egress) data traffic, allowing or blocking connections based on predefined rules.
Firewall Profiles: Domain, Private and Public
Windows firewall has three main profiles that determine how the firewall behaves in different network conditions. These profiles are "Domain", "Private", and "Public". The settings for each profile can be configured separately to provide the appropriate level of protection depending on where and how the computer is used. Here's an explanation for each profile:
Domain profile
Domain profile is active when a computer is connected to a company or organization network that uses Active Directory management.
Private profile
The private profile is intended for use in trustworthy private networks, such as home networks or small business networks.
Public profile
Public (public) profile is intended for use in public networks, such as cafes, libraries, or airport Wi-Fi networks, which are not trusted.
How does Windows know if the network is private or public?
Windows does not know if you are connected to a Wi-Fi network in a cafe or in your home network. So, when you connect your computer to a new network, Windows usually asks if you trust this network or not. At this point, you can choose whether to keep the network public or private.
Domain profile can be deduced automatically from an Active Directory domain (a topic which is not covered in depth in this course).
Checking and enabling the state of Windows Firewall
Windows Firewall Management
Opening a Firewall
You can open the firewall settings by typing "Windows Defender Firewall" into the Windows search bar and selecting the appearing application.
Checking Firewall Status
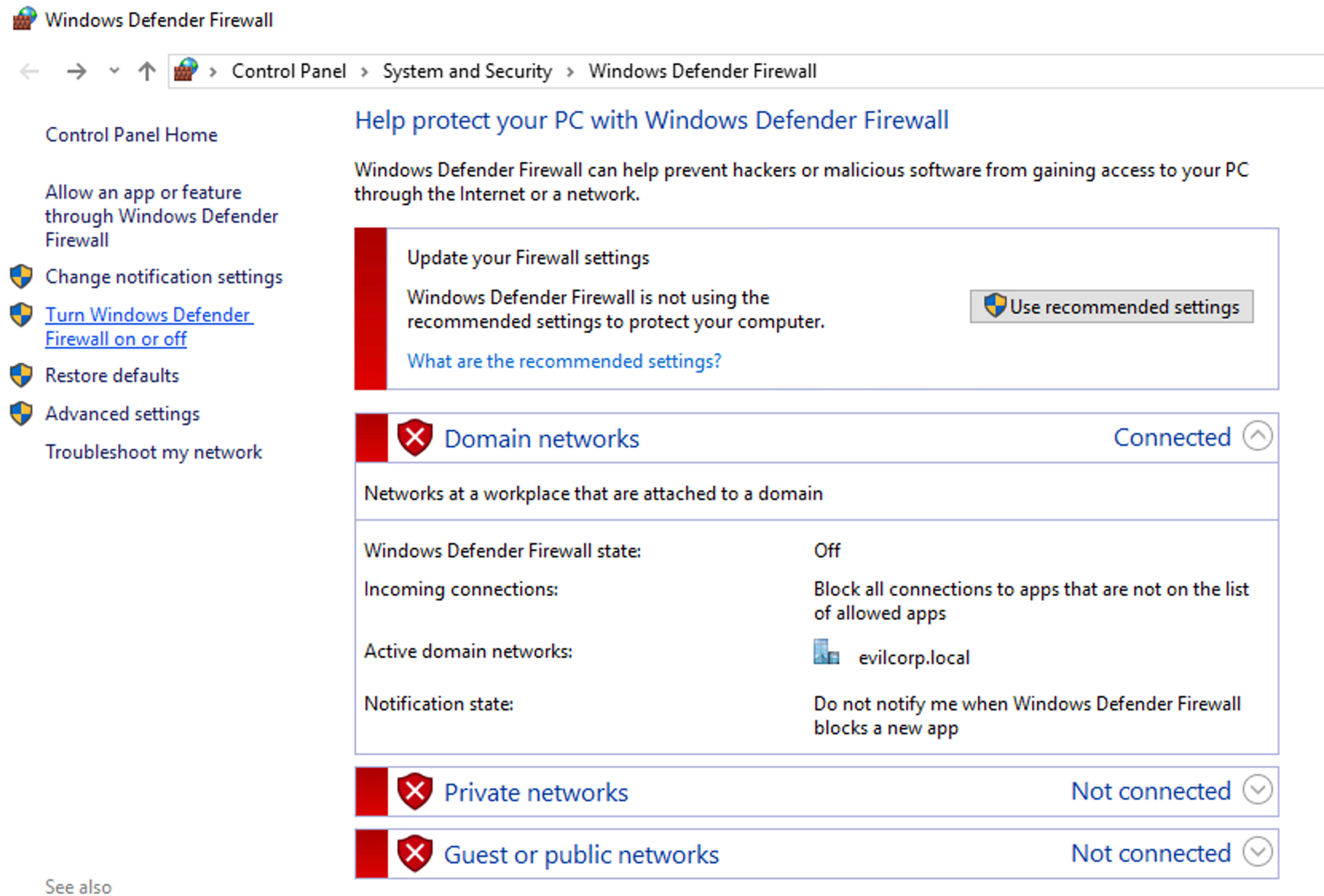
Check the status of the firewall to ensure that it is enabled.
Enabling Firewall
If the firewall is not in use, you can enable it by clicking on the button "Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off".
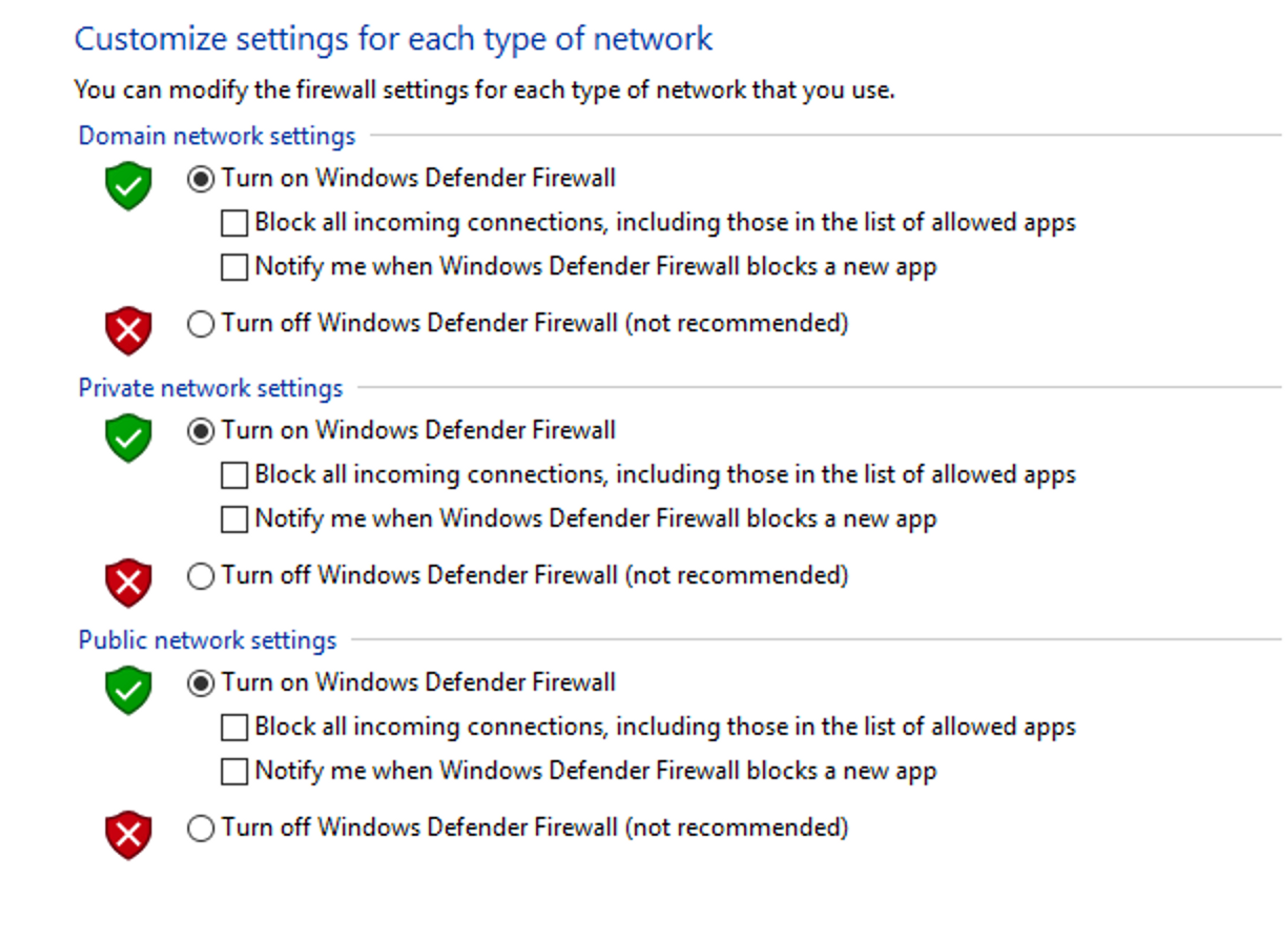
Creating a New Rule:
- Select "Advanced settings" to access additional management options and navigate to "Inbound Rules" or "Outbound Rules" to add new rules.
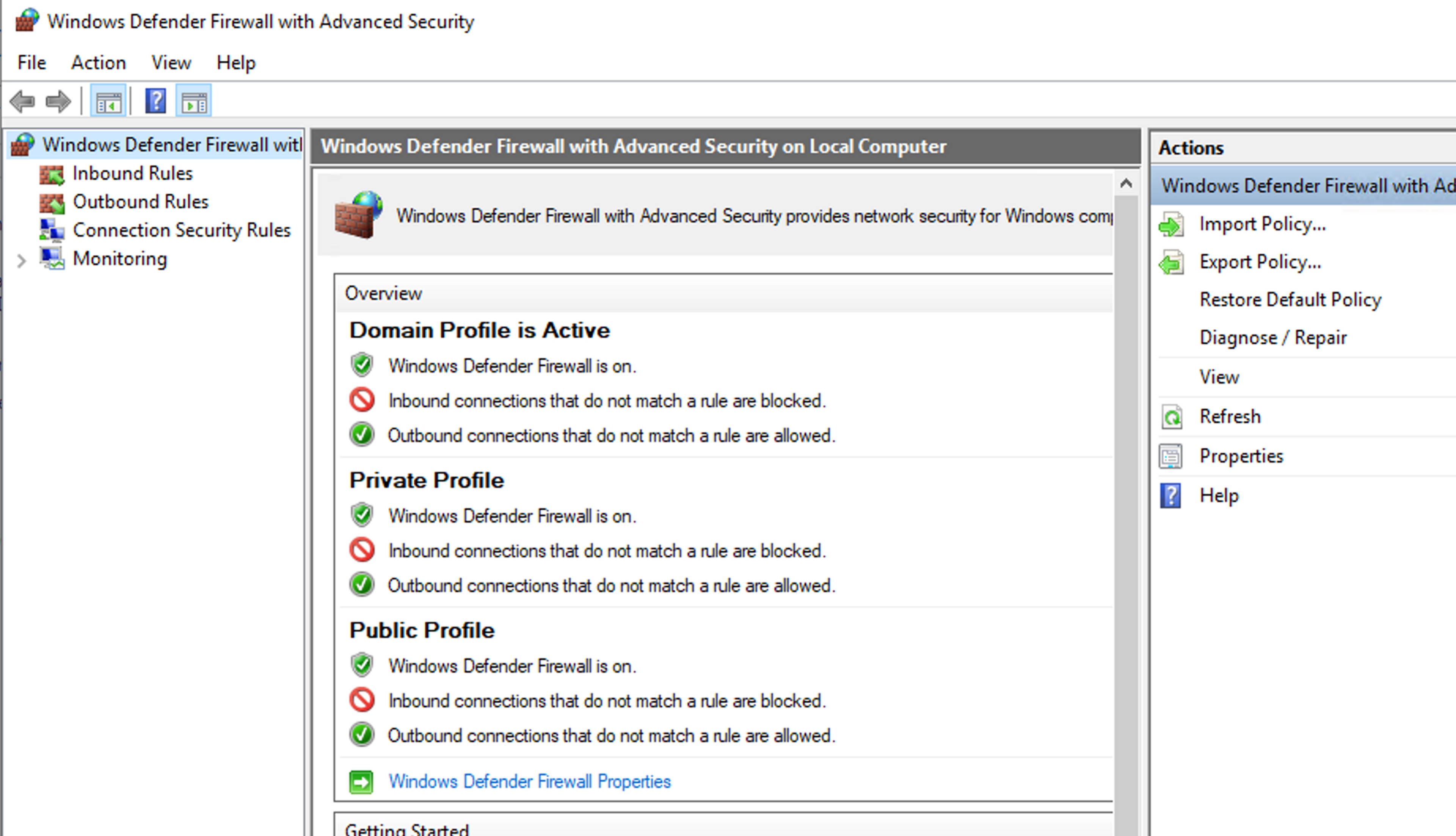
- Click "New Rule" to create a new rule. You can create a rule for a program, a port, a specific service, or a custom rule.
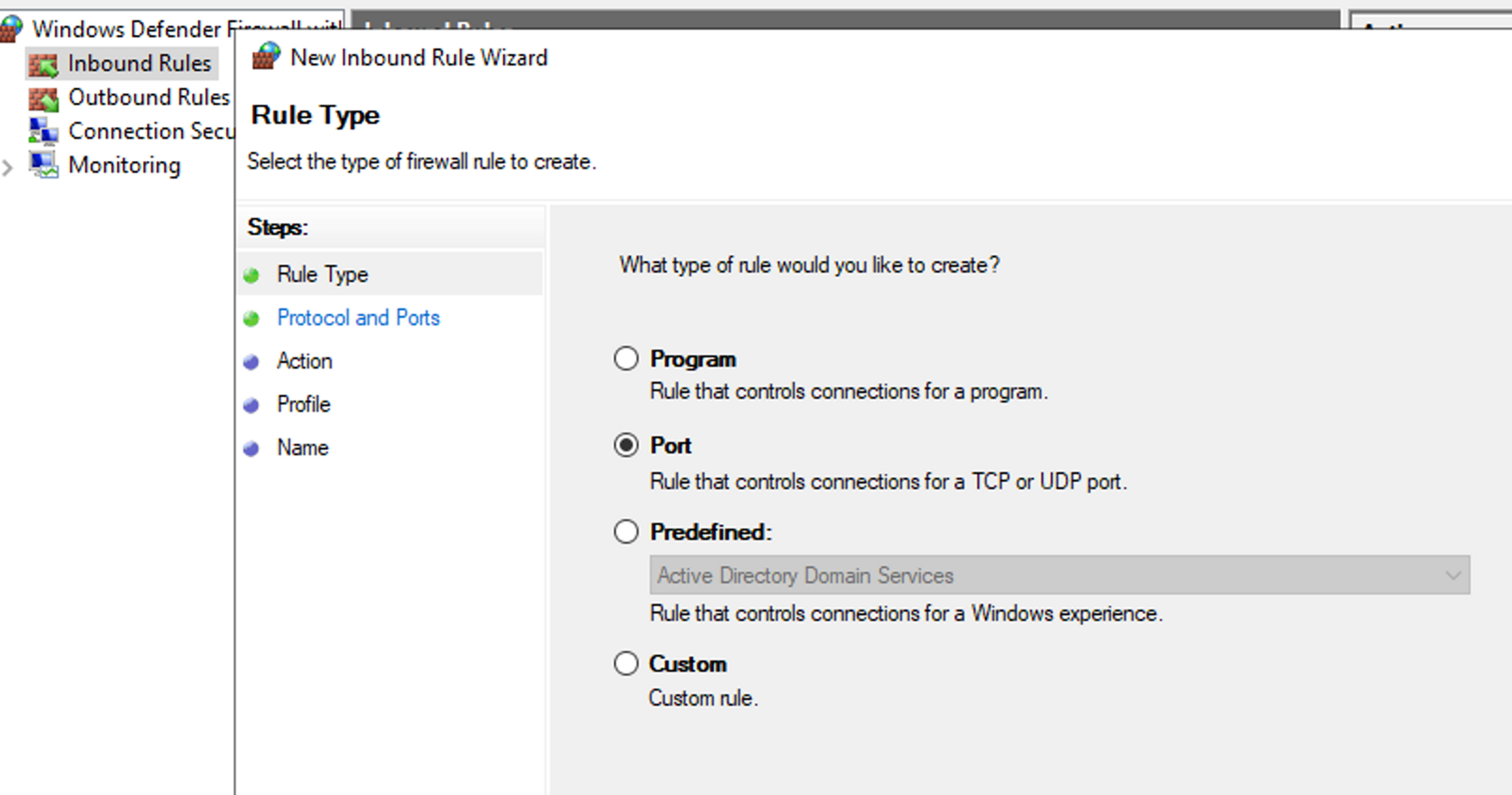
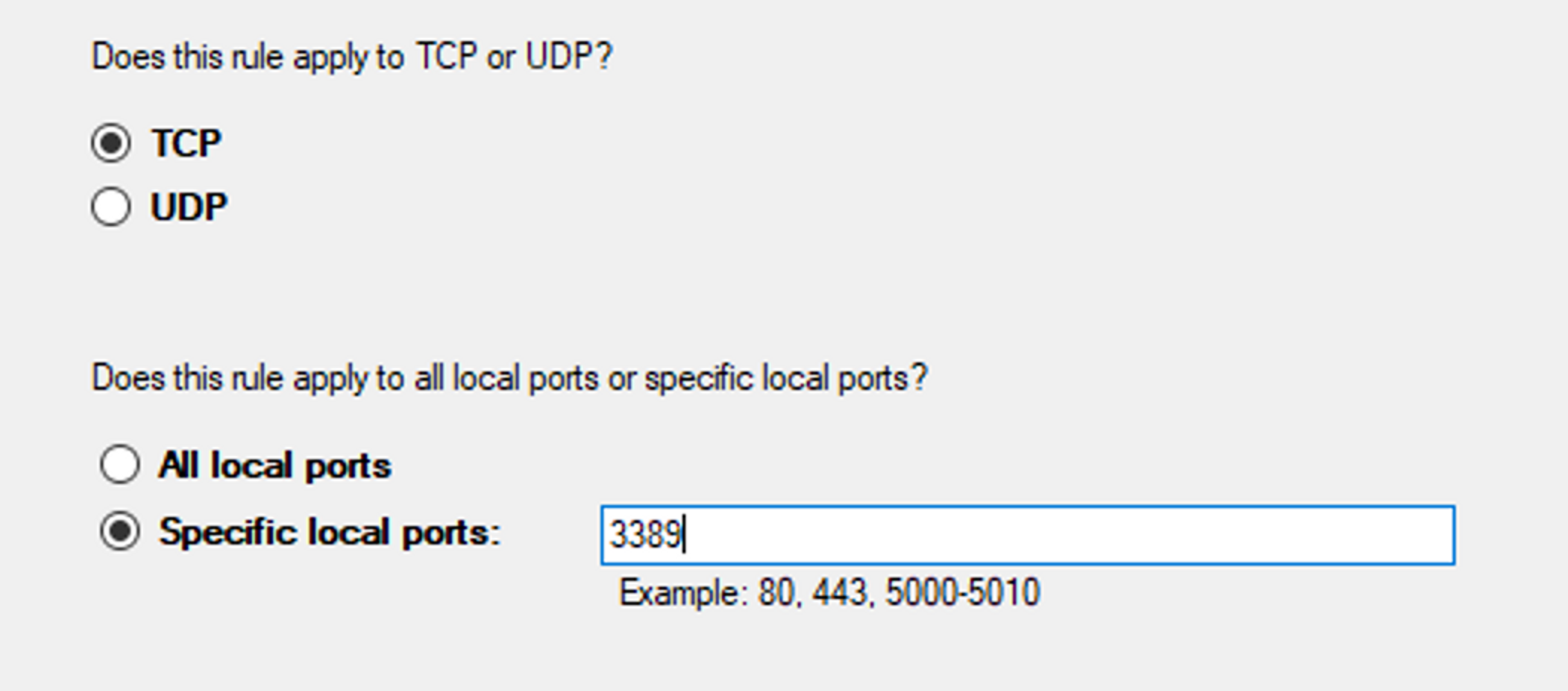
- Define the rule settings, for example in the case of a port, which port is in question.
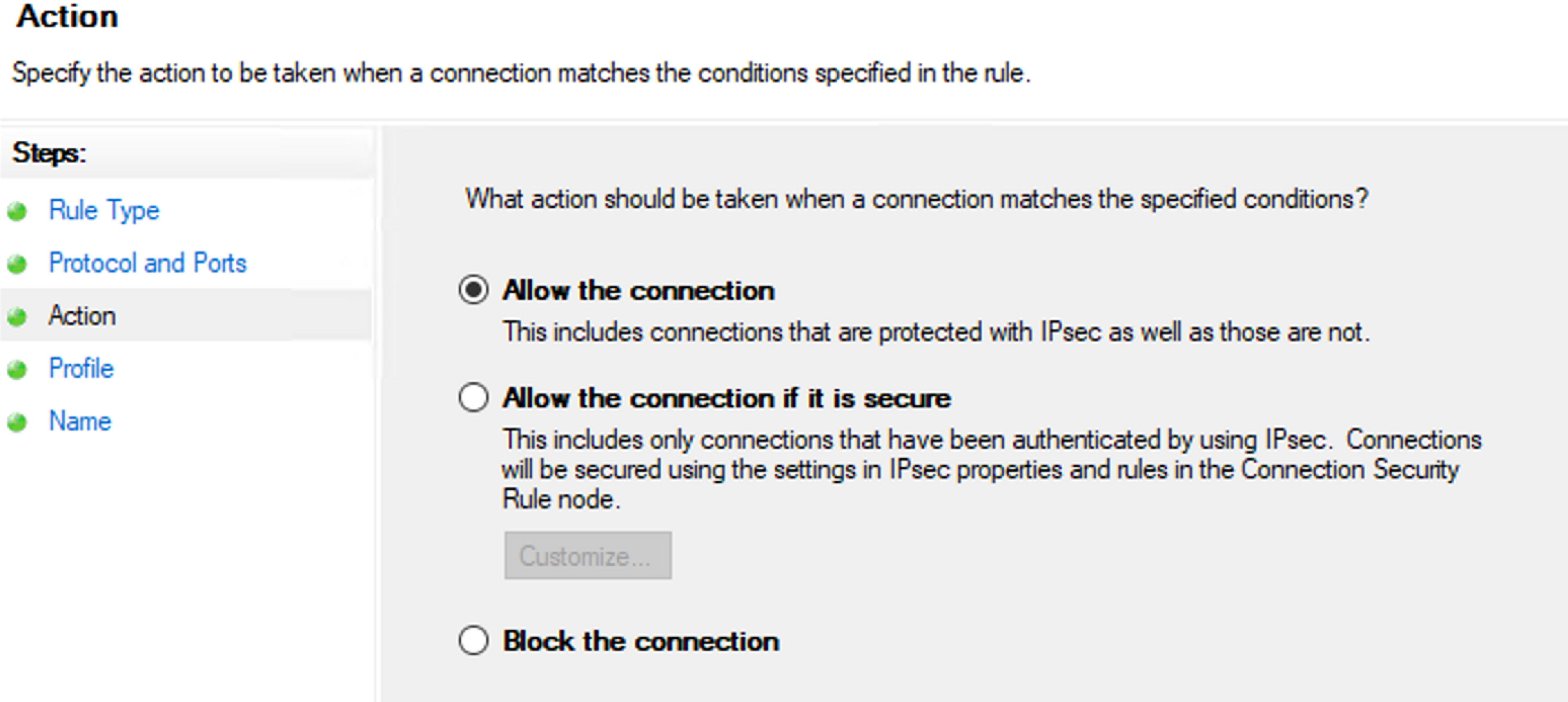
- Tell Windows how to act when this kind of connection is detected. Should it be allowed or blocked (or only allowed within an IPSec tunnel)?
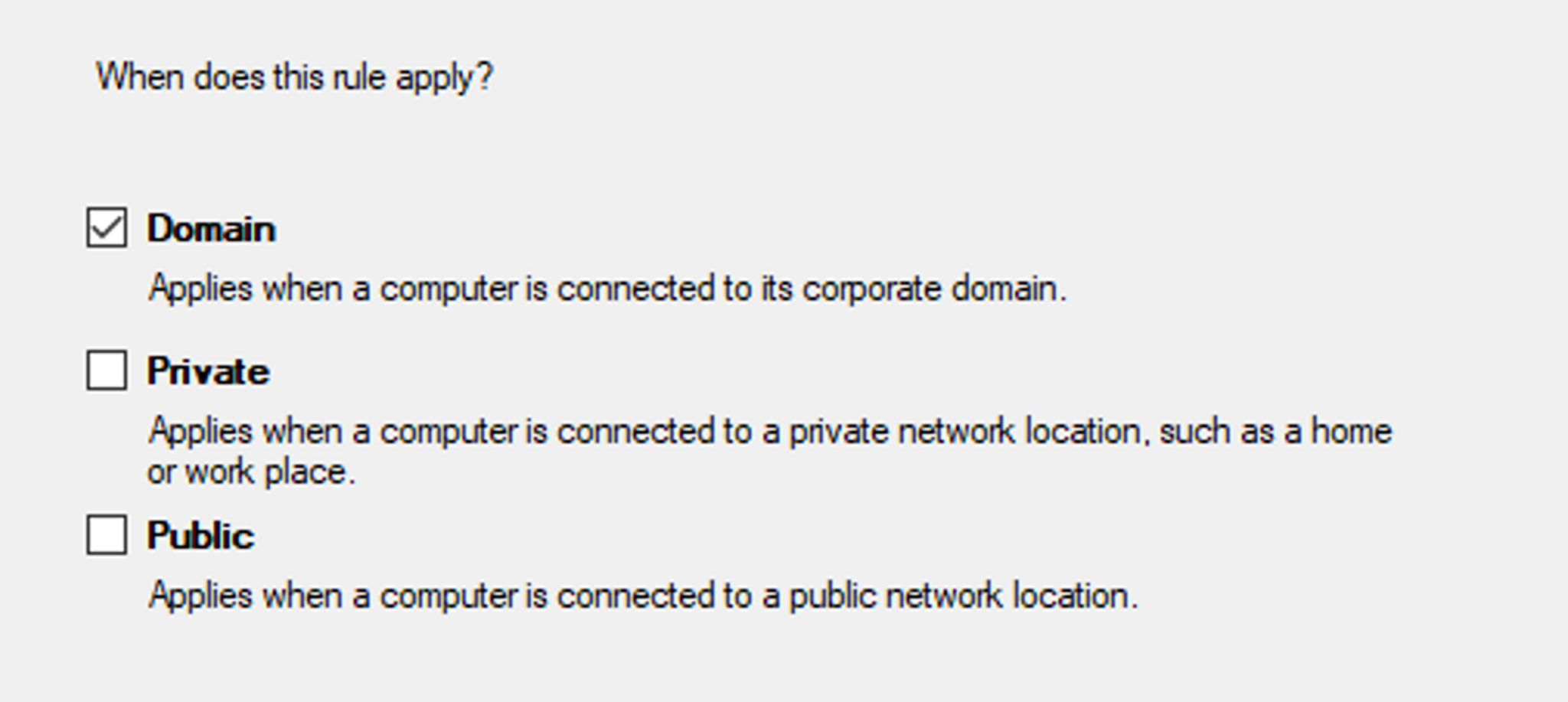
- Specify which profiles you want the rule to apply to.
- Finally, give a name and description to the rule.
Modifying or Deleting Rules:
If you want to edit or delete an existing rule, you can do so by navigating to that rule in the Advanced settings view, right-clicking it, and selecting "Properties" or "Delete".
Tasks
Enable Windows Firewall
Enable Windows firewall (turn it on). When that is done, run Check.ps1 and enter flag 1.
Ticket 1
Open TCP port 80 to the Internet
You are asked to open TCP port 80 (HTTP) so that a web application can be installed on the server. Open the port, then run Check.ps1 and enter flag 2.
Ticket 2


Ready to become an ethical hacker?
Start today.
As a member of Hakatemia you get unlimited access to Hakatemia modules, exercises and tools, and you get access to the Hakatemia Discord channel where you can ask for help from both instructors and other Hakatemia members.



